EB-5 Visa Tax
Boost Your Freedom Without Compromise.
- Who offers the CHEAPEST program available.
- Who offers the BEST program available.
- What you need to qualify?

Securing a U.S. green card through the EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program is a major milestone, but it comes with complex tax responsibilities. Understanding U.S. tax residency, global income reporting, and strategic planning is crucial for protecting your wealth and ensuring compliance. This guide provides up-to-date, expert-backed insights to help EB-5 investors navigate U.S. tax rules and optimize their financial outcomes.
For a broader look at global investment migration, explore the WorldPassports citizenship by investment overview.
- EB-5 investors may become U.S. tax residents, subject to worldwide income tax and strict reporting requirements.
- Common challenges include double taxation, estate and gift tax exposure, and compliance with FBAR and FATCA.
- Pre-immigration tax planning can significantly reduce long-term liabilities.
- Tax treaties and asset restructuring may offer relief for some investors.
- Understanding the Substantial Presence Test is essential for compliance and effective planning.
Have you considered the EB-5 visa tax implications that could dramatically impact your financial circumstances?
Surprisingly, many people overlook the fact that, as an EB-5 visa holder, you become liable for tax on your worldwide income.
In This Article, You Will Discover:
With a commitment to reliable, accurate information, we demystify these complexities so that you have the knowledge you need to further your EB-5 journey.
Stay with us to explore valuable strategies for efficiently managing your taxes on the EB-5 visa journey.
*Disclaimer: All amounts quoted in this article were correct and accurate at the time of publication and may have shifted since.
- Who offers the CHEAPEST program available.
- Who offers the BEST program available.
- What you need to qualify?
 Free Consultation
Free Consultation Easy to Use
Easy to Use 100% Safe & Secure
100% Safe & Secure
Common Tax Challenges for EB-5 Visa Investors
Entering the U.S. as an EB-5 investor opens doors to opportunity, but also introduces several tax pitfalls. Each point below is introduced with a brief overview to help you anticipate and address these challenges.
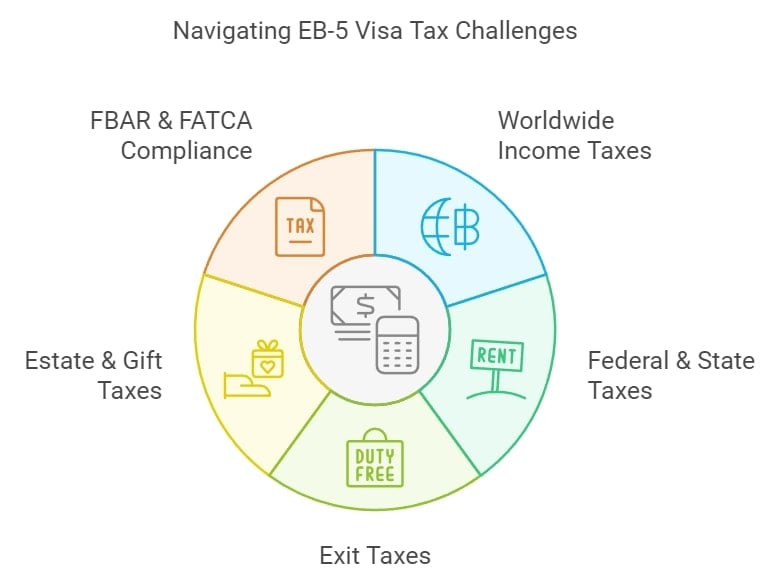
Worldwide Income Taxation
Once you become a U.S. tax resident, you are required to report and pay tax on your global income—including employment, rental, investment, and business income from outside the U.S. This can be particularly complex for investors with diverse international assets.
Federal and State Income Taxes
U.S. tax residents are subject to both federal and, in most cases, state income taxes. While federal rates are uniform, state taxes vary widely. States like Florida and Texas have no state income tax, while California and New York impose some of the highest rates. Your choice of residence can significantly impact your overall tax burden.
Exit Tax on Relinquishing Residency
If you decide to give up your U.S. permanent residency, you may face an "exit tax" on the net unrealized gain of your worldwide assets. This tax generally applies to individuals with a net worth over $2 million or those with high average annual income tax liability over the previous five years.
Estate and Gift Tax Exposure
U.S. tax residents are subject to estate and gift taxes on all assets, regardless of location. This can affect wealth transfer and inheritance planning for families with global holdings.
FBAR and FATCA Reporting
EB-5 investors must comply with the Foreign Bank Account Report (FBAR) and the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA). This means declaring foreign bank accounts and financial assets to the U.S. Treasury. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, including fines up to $100,000 or 50% of the account balance for willful violations.
Can the EB-5 Visa Offer Tax Advantages?
Despite the obligations, the EB-5 visa can provide certain tax benefits. Each point below is introduced with a short explanation to clarify its relevance.
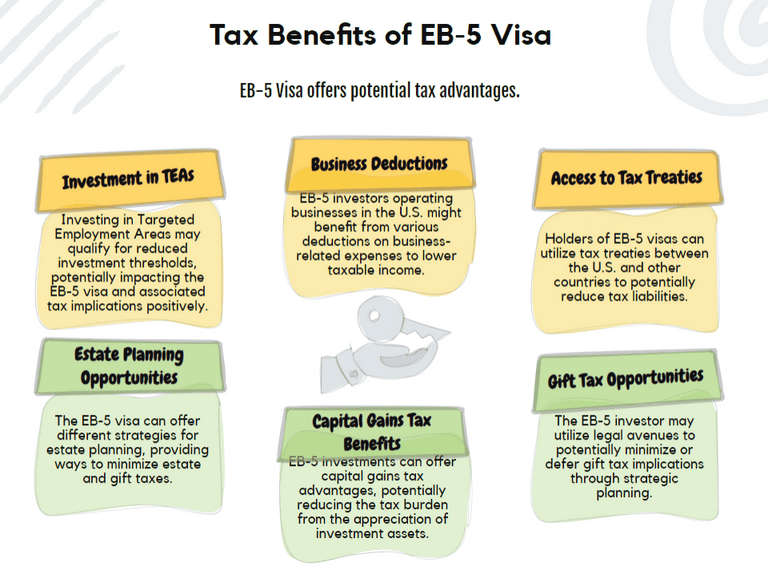
Investment in Targeted Employment Areas (TEAs)
Investing in a TEA can lower the minimum investment threshold, potentially reducing your capital at risk and associated tax liabilities.
Access to Tax Treaties
Many countries have tax treaties with the U.S. to prevent double taxation. These treaties can reduce or eliminate U.S. tax on certain types of income, such as dividends or interest, and may provide tie-breaker rules for dual residents.
Business Deductions
If your EB-5 investment is structured as a business, you may be eligible for various deductions, including business expenses and startup costs. Proper structuring and professional advice are essential to maximize these benefits.
Estate and Gift Tax Planning
With careful planning, EB-5 investors can take advantage of U.S. rules that may exempt certain gifts or inheritances from taxation, especially those received from non-U.S. residents.
Capital Gains Tax Rates
Long-term capital gains (on assets held over a year) are typically taxed at lower rates than ordinary income, which can benefit investors whose EB-5 investments appreciate over time.
Tax Strategies for Managing EB-5 Liabilities
Effective tax planning is essential for EB-5 investors. The following strategies, each with a brief introduction, can help you minimize liabilities and avoid costly mistakes.
Pre-Immigration Tax Planning
Consult a cross-border tax advisor before applying for your EB-5 visa. Strategies may include restructuring foreign assets, establishing trusts, or leveraging gifting opportunities to optimize your U.S. tax position.
State Tax Considerations
Research state income tax laws before choosing where to reside in the U.S. Some states offer significant tax advantages for new residents.
Leveraging Tax Treaties and Credits
Take advantage of tax treaties and the U.S. foreign tax credit to avoid double taxation on income earned abroad.
Compliance with Reporting Requirements
Ensure timely and accurate filing of FBAR and FATCA forms. Maintain detailed records of all foreign accounts and assets to avoid penalties.
Considering Alternative Visa Options
If the EB-5 tax implications are too burdensome, explore alternatives such as the E-2 visa, which may offer more favorable tax outcomes depending on your circumstances. For a comparison, see the pros and cons of citizenship by investment.
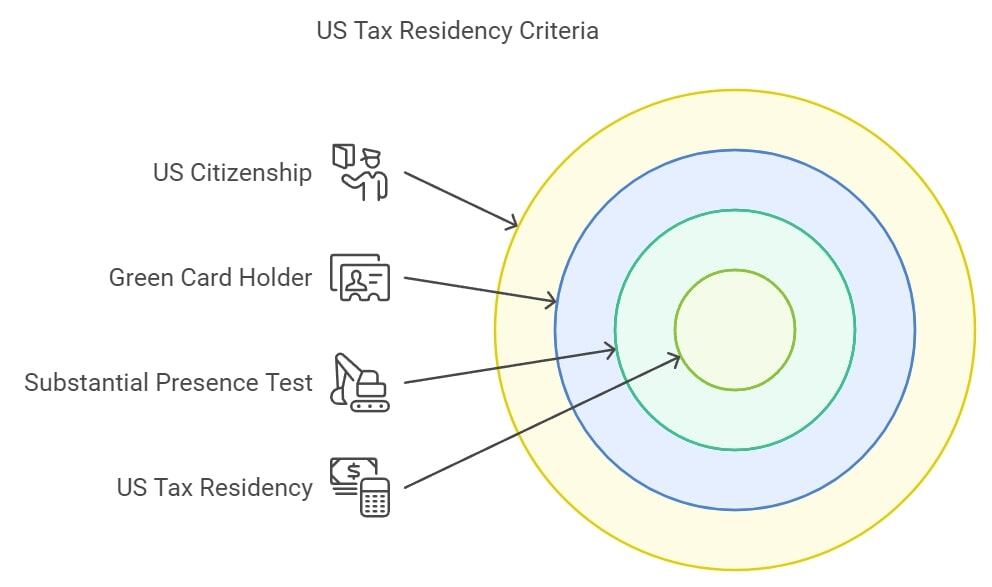
Understanding U.S. Tax Residency: The Substantial Presence Test
Becoming a U.S. tax resident triggers global tax obligations. There are three main ways to qualify:
- U.S. Citizenship: Automatically confers tax residency.
- Green Card Holder: Holding a green card makes you a tax resident, regardless of time spent in the U.S.
- Substantial Presence Test: If you spend at least 31 days in the U.S. in the current year and a total of 183 days over the current and previous two years (using a weighted formula), you may be classified as a tax resident. Certain days, such as brief transits or time as a student, may be excluded.
Common Questions
What’s the Substantial Presence Test?
What’s the FBAR Form?
What’s FATCA 8938?
Do Foreigners Working in the USA Pay Taxes?
Do Green Card Holders Have to Pay Tax to the US?
How Can You Live in the US Without Paying Tax?
How Can I Avoid Being a US Tax Resident?
In Conclusion
Navigating EB-5 visa tax responsibilities requires careful planning, expert advice, and ongoing compliance. By understanding your obligations, leveraging available tax benefits, and working with experienced professionals, you can protect your wealth and achieve your U.S. residency goals with confidence. For more insights and the latest updates, visit the WorldPassports EB-5 visa tax planning hub.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Tax laws and regulations are subject to change. Always consult a qualified tax advisor before making investment or residency decisions.
- Who offers the CHEAPEST program available.
- Who offers the BEST program available.
- What you need to qualify?
 Free Consultation
Free Consultation Easy to Use
Easy to Use 100% Safe & Secure
100% Safe & Secure





